
: 34–36 The same ship was used for the link from Dover to Ostend in Belgium, by the Submarine Telegraph Company. : 361 The British & Irish Magnetic Telegraph Company completed the first successful Irish link on May 23 between Portpatrick and Donaghadee using the collier William Hutt. In 1853, more successful cables were laid, linking Great Britain with Ireland, Belgium, and the Netherlands, and crossing The Belts in Denmark. : 192–193 However, the experiment served to secure renewal of the concession, and in September 1851, a protected core, or true, cable was laid by the reconstituted Submarine Telegraph Company from a government hulk, Blazer, which was towed across the Channel. It was simply a copper wire coated with gutta-percha, without any other protection, and was not successful. In August 1850, having earlier obtained a concession from the French government, John Watkins Brett's English Channel Submarine Telegraph Company laid the first line across the English Channel, using the converted tugboat Goliath. : 26–27 First commercial cables A telegraph stamp of the British & Irish Magnetic Telegraph Co. In 1849, Charles Vincent Walker, electrician to the South Eastern Railway, submerged 3 km (2 mi) of wire coated with gutta-percha off the coast from Folkestone, which was tested successfully. In 1847 William Siemens, then an officer in the army of Prussia, laid the first successful underwater cable using gutta percha insulation, across the Rhine between Deutz and Cologne.
Michael Faraday and Wheatstone soon discovered the merits of gutta-percha as an insulator, and in 1845, the latter suggested that it should be employed to cover the wire which was proposed to be laid from Dover to Calais. : 26–27 Twenty years earlier, Montgomerie had seen whips made of gutta-percha in Singapore, and he believed that it would be useful in the fabrication of surgical apparatus. Gutta-percha, the adhesive juice of the Palaquium gutta tree, was introduced to Europe by William Montgomerie, a Scottish surgeon in the service of the British East India Company. India rubber had been tried by Moritz von Jacobi, the Prussian electrical engineer, as far back as the early 19th century.Īnother insulating gum which could be melted by heat and readily applied to wire made its appearance in 1842. A good insulator to cover the wire and prevent the electric current from leaking into the water was necessary for the success of a long submarine line. The following autumn, Wheatstone performed a similar experiment in Swansea Bay. Samuel Morse proclaimed his faith in it as early as 1840, and in 1842, he submerged a wire, insulated with tarred hemp and India rubber, in the water of New York Harbor, and telegraphed through it.
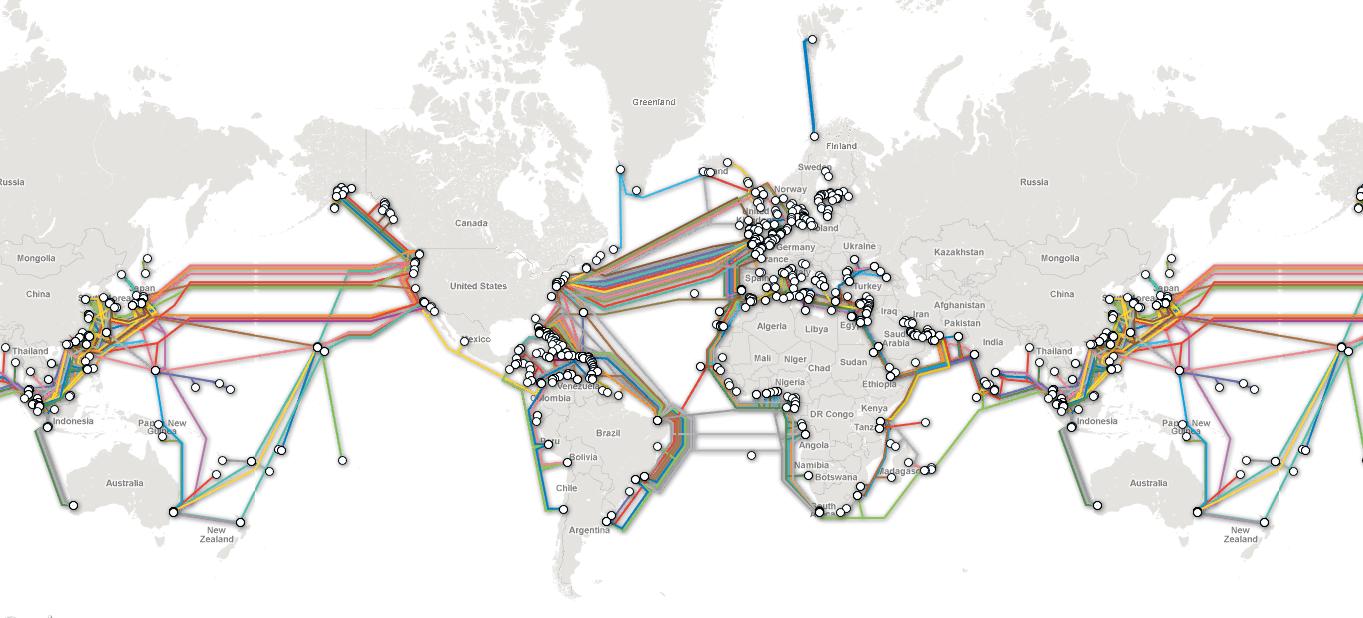
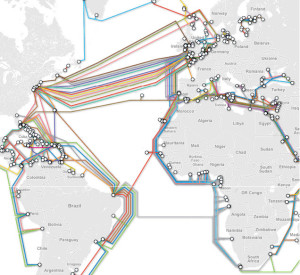
Early history: telegraph and coaxial cables First successful trials Īfter William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone had introduced their working telegraph in 1839, the idea of a submarine line across the Atlantic Ocean began to be thought of as a possible triumph of the future. Modern cables are typically about 25 mm (1 in) in diameter and weigh around 1.4 tonnes per kilometre (2.5 short tons per mile 2.2 long tons per mile) for the deep-sea sections which comprise the majority of the run, although larger and heavier cables are used for shallow-water sections near shore. These early cables used copper wires in their cores, but modern cables use optical fiber technology to carry digital data, which includes telephone, Internet and private data traffic. Subsequent generations of cables carried telephone traffic, then data communications traffic. Submarine cables first connected all the world's continents (except Antarctica) when Java was connected to Darwin, Northern Territory, Australia, in 1871 in anticipation of the completion of the Australian Overland Telegraph Line in 1872 connecting to Adelaide, South Australia and thence to the rest of Australia.

The first submarine communications cables laid beginning in the 1850s carried telegraphy traffic, establishing the first instant telecommunications links between continents, such as the first transatlantic telegraph cable which became operational on 16 August 1858. A cross section of the shore-end of a modern submarine communications cable.Ĩ – Optical fibers Submarine cables are laid using special cable layer ships, such as the modern René Descartes, operated by Orange Marine.Ī submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the sea bed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea. Not to be confused with submarine power cable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
